Introduction
In today’s data-driven landscape, businesses are embracing cloud computing technology for its efficiency and scalability. A Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) report revealed that 98% of organizations worldwide use cloud services. Yet, more than 1/3rd of those organizations may not be using key security frameworks like CSA’s CCM and CAIQ, which raises questions about how they are managing cloud security and risk. And the potential repercussions of cloud compliance failure range from steep financial penalties and lawsuits to loss of competitive advantage and reputational damage to greater risk of security incidents like data breaches.
That’s why understanding cloud compliance has become a critical priority as more organizations transition to cloud-based systems. In this blog, we will explore the importance of cloud compliance, review some common frameworks, and outline 10 best practices to help organizations ensure they remain secure and compliant in the cloud.
Is Your Organization Equipped to Tackle the Evolving Challenges of Cloud Compliance?
Many organizations manage large amounts of data, including personal information and business-critical data. Regulations must be adhered to, not only to meet regulatory requirements and conduct business in various geographies and certain industries but also to maintain security, privacy, and business integrity. With cyber threats on the rise, especially those targeting cloud infrastructures, maintaining compliance is vital for safeguarding sensitive information, building customer trust, and protecting overall business operations.
What Is Cloud Compliance?
Cloud compliance refers to the process of adhering to specific regulatory standards, legal mandates, and industry-recognized best practices in cloud computing. It ensures that cloud-based services, applications, and data meet essential security, privacy, and operational requirements. Organizations must navigate a wide range of compliance frameworks, such as CIS, NIST, MITRE ATT&CK®, and ISO, alongside regulations like GDPR, FedRAMP, and HIPAA. These frameworks and regulations are designed to safeguard data, ensure privacy, and uphold security standards, which are critical for building and maintaining customer trust.
Achieving cloud compliance requires strong security measures, regular audits, and continuous monitoring to defend against potential breaches and ensure ongoing regulatory alignment. As the compliance landscape evolves to keep up with the rapid growth in data collection, new benchmarks and regulations emerge, addressing a broader spectrum of challenges. These range from data privacy and cybersecurity to financial reporting and environmental standards. Organizations must keep abreast of the latest regulations and frameworks to stay compliant.
The Importance of Cloud Compliance
Cloud compliance is crucial for organizations operating in cloud environments, as it ensures that they adhere to necessary regulations, protect sensitive data, and maintain the trust of customers and partners. Here are key reasons why cloud compliance is essential.
- Data Security and Privacy: Cloud compliance frameworks help organizations safeguard sensitive information, including customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. Compliance ensures the implementation of robust security controls, such as encryption, access management, and incident response, to protect this data from breaches, unauthorized access, or cyber threats.
- Legal Implications:
Non-compliance with major regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, can result in severe legal repercussions. Organizations may face fines, sanctions, and lawsuits for failing to protect data or violating privacy laws. Cloud compliance ensures businesses meet the legal standards required to operate safely in regulated industries and avoid these costly penalties. - Reputation and Trust:
Organizations must demonstrate to customers, partners, and stakeholders that their data is managed securely in the cloud. Compliance with recognized standards, such as ISO 27001 or CIS Benchmarks, assures that the organization prioritizes data security and privacy. This, in turn, fosters trust, enhances customer loyalty, and strengthens the organization’s reputation. - Market Competitiveness: In a competitive marketplace, compliance can be a key differentiator. Businesses that adhere to strict cloud compliance standards often gain an advantage over non-compliant competitors, as they are perceived as more secure, reliable, and trustworthy. Being compliant not only helps attract new customers but can also open opportunities for partnerships with other organizations that prioritize security and compliance.
By ensuring cloud compliance, organizations protect their assets, stay within legal boundaries, maintain customer trust, and position themselves as leaders in a highly competitive digital landscape.
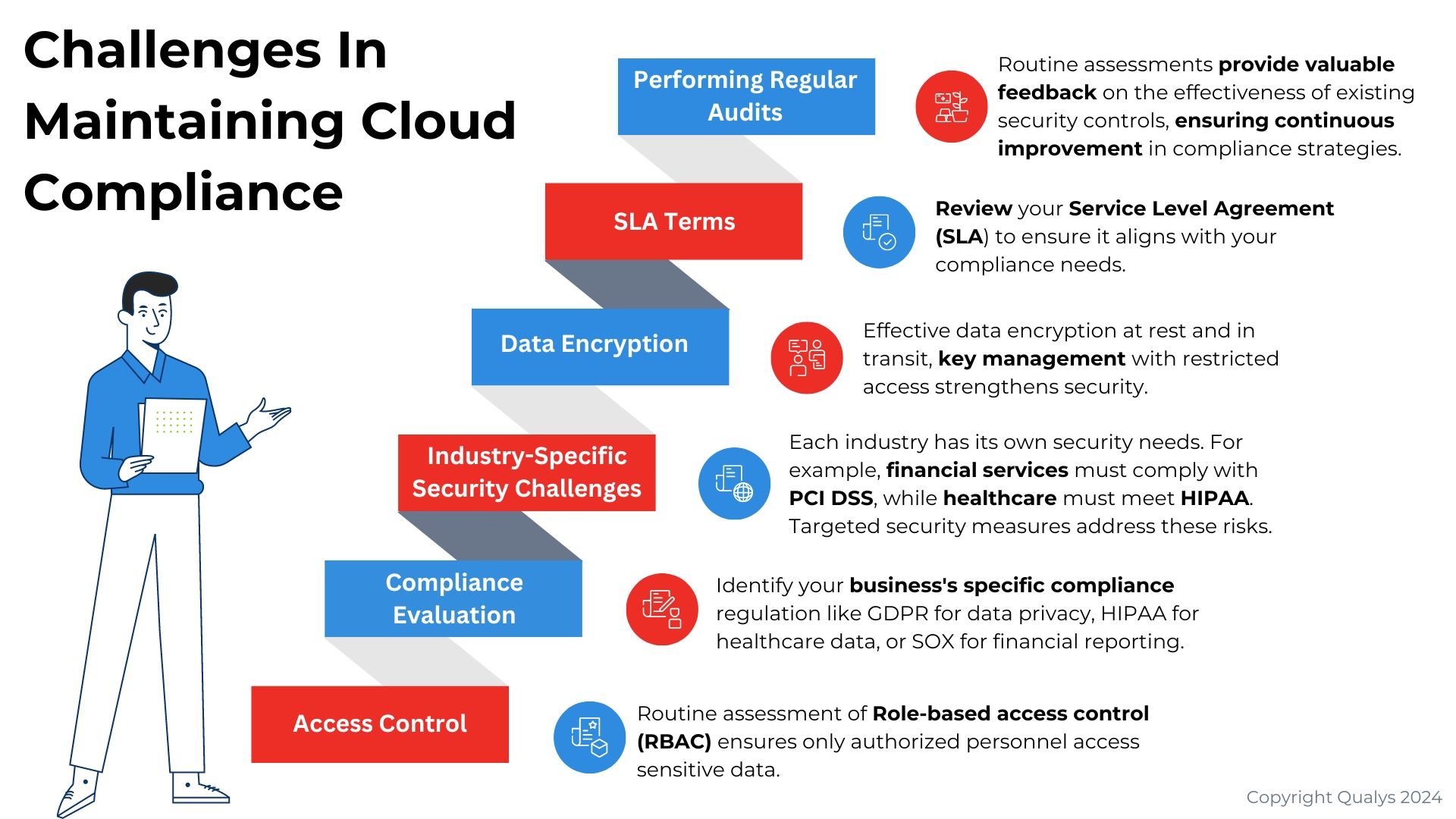
Common Cloud Regulations and Standards
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European Union Law that enhances privacy and gives individuals control over their personal data. For cloud computing, GDPR has specific implications, as mentioned below, that organizations must address to ensure compliance:
- Roles: Data controllers (organizations) are responsible for compliance, while cloud providers act as data processors.
- Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): Conduct DPIAs for high-risk cloud processing.
- Data Transfer and Location: Safeguards transferring of data outside the EU.
- Data Security and Privacy: Implement strong security measures, including encryption and access controls.
- Breach Notification: Notify authorities and affected individuals of breaches promptly.
- Contracts: Establish clear Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) with cloud providers.
GDPR compliance in the cloud demands thorough planning, clear agreements, and continuous monitoring to safeguard personal data and privacy rights.
Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) and NIST SP 800-53
FedRAMP and NIST SP 800-53 together set security standards for U.S. federal cloud services. FedRAMP ensures that cloud service providers (CSPs) meet NIST-based security controls. It adapts these controls for cloud environments, categorizing data sensitivity (Low, Moderate, High) and requiring ongoing monitoring.
ISO 27000 family of standards
The ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards is a set of internationally recognized frameworks for managing information security. These standards provide best practices and guidelines to help organizations safeguard their information assets, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Key standards in the family include:
- ISO/IEC 27001: Specifies requirements for an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
- ISO/IEC 27002: Provides guidelines and best practices for implementing security controls outlined in ISO 27001.
- ISO/IEC 27005: Focuses on risk management within the context of information security, offering a methodology to assess and treat security risks.
- ISO/IEC 27017: Specifies information security controls applicable to cloud services.
- ISO/IEC 27018: Focused on protecting personal data in the cloud.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a set of standards to protect credit card information and prevent fraud. Key requirements include:
- Secure Network: Implement firewalls and secure passwords.
- Data Protection: Encrypt cardholder data during transmission across open, public networks.
- Implement Strong Access Control Measures: Restrict access to cardholder data to only those who need it.
- Monitor and Test Networks: Track network access and test security systems.
- Maintaining an Information Security Policy: Establish and maintain a company-wide policy on information security.
Compliance with PCI DSS helps organizations protect payment data, reduce fraud, and build trust with customers. It is mandatory for any organization that handles credit card transactions.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a U.S. law that protects individuals’ medical information, known as Protected Health Information (PHI). HIPAA establishes standards for how healthcare providers, insurance companies, and other entities handle sensitive patient data.
Key components of HIPAA include:
- Privacy Rule: Regulates the use and disclosure of PHI by covered entities (healthcare providers, insurers, etc.), ensuring that individuals’ health information is kept confidential and shared only when necessary.
- Security Rule: Requires for electronic PHI (ePHI).
- Breach Notification Rule: Mandates notification in the event of a breach.
- Enforcement Rule: Imposes penalties for non-compliance. HIPAA compliance ensures that healthcare organizations protect patient data and uphold privacy standards while also reducing the risk of data breaches and misuse of sensitive health information.
Most Common Cloud Security Frameworks
Security frameworks provide structured approaches to managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks, offering guidance and best practices for safeguarding systems and data. They help organizations identify vulnerabilities, implement protective measures, and ensure compliance with security requirements.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF)
This framework offers a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks by providing guidelines for identifying, protecting against, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber threats. It is designed to be flexible and adaptable, allowing organizations to tailor its components to their specific needs and risk profiles.
Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM)
The CCM is a framework specifically for evaluating cloud service providers’ security controls. It consists of a set of security principles and controls that cover various domains, helping organizations assess the security posture of cloud services and ensure they meet necessary security requirements.
Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls
The CIS Controls are a set of best practices aimed at improving cybersecurity across different environments, including cloud. They provide actionable recommendations and controls to help organizations strengthen their defenses against common cyber threats and vulnerabilities. The controls are designed to be practical and effective, focusing on key areas such as asset management, access control, and incident response.
MITRE ATT&CK for Cloud
This framework extends the MITRE ATT&CK matrix to address tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by adversaries in cloud environments. It helps organizations understand the threats and attack vectors specific to cloud computing, providing a comprehensive view of how attackers might exploit cloud infrastructures and offering guidance on how to detect and mitigate these threats.
Cloud Compliance Best Practices
Cloud compliance best practices ensure your cloud environment adheres to security, regulatory, and industry standards. Here are some generic best practices:
- Understand Relevant Regulations
- Identify the laws and regulations that apply to your industry (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS) and ensure your cloud environment aligns with them.
- Conduct regular reviews to stay compliant with evolving regulations.
- Implement Data Encryption
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to safeguard it from unauthorized access.
- Use encryption keys securely managed by either the cloud provider or your organization.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring users have access only to the resources they need.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced security.
- Regularly audit and review user permissions.
- Continuous Monitoring and Logging
- Use real-time monitoring tools to detect and respond to security incidents.
- Enable logging for all activities and ensure logs are protected and easily accessible for audits.
- Establish Data Residency and Governance Policies
- Ensure compliance with data residency requirements (e.g., storing data in specific geographical regions).
- Implement policies for data lifecycle management, such as retention and deletion processes.
- Regular Audits and Assessments
- Perform regular internal audits and third-party assessments to ensure cloud environments remain compliant.
- Conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and address potential risks.
- Leverage Cloud Compliance Tools
- Use built-in or third-party tools like AWS Config, Azure Policy, or Google Cloud Security Command Center to manage compliance.
- Automate compliance monitoring to reduce human error and ensure continuous alignment with regulatory requirements.
- Third-Party Risk Management
- Assess cloud service providers’ compliance certifications (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001) and ensure they meet your organization’s standards.
- Establish clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs) outlining the provider’s responsibility for compliance and data protection.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Implement automated, secure backup strategies to protect data and ensure business continuity.
- Regularly test disaster recovery plans to ensure data can be recovered in case of a breach or failure.
- Employee Training and Awareness
- Regularly train employees on cloud security and compliance policies.
- Ensure that employees are aware of the latest best practices for managing sensitive data in the cloud.
Following these best practices helps ensure your cloud operations remain secure, compliant, and ready for audits, minimizing the risk of regulatory violations.
How TotalCloud Helps You Maintain Cloud Compliance
Qualys TotalCloud, a CNAPP (Cloud Native Application Protection Platform) that rigorously adheres to cloud security best practices, helps to continuously monitor compliance with versatile reporting and CIS benchmarks. Compliance with various industry mandates is essential for many regulated businesses. The TotalCloud Compliance Posture dashboard always provides an up-to-date view of your compliance posture for any of the 30+ industry mandates. It also highlights critical misconfigurations, like MFA not being enabled, that have been used for exploits.
The TotalCloud dashboard amalgamates all the critical data harvested from the Qualys platform and presents it in a single place. With the TotalCloud dashboard, you can visualize your organization’s multi-cloud security posture and gain instant insights into cloud infrastructure and workload exposures.
Mandate Compliance Standards Supported in TotalCloud
Mandates are regulatory requirements, best practice standards, or compliance frameworks designed by security- and business-driven certification communities and/or government bodies.
Launch the Mandate-based Report to view the organization’s compliance posture in terms of the underlying Security baseline against selected Mandates. This allows you to choose any mandates you must comply with and get a view of compliance posture in terms of their selected policies.
We support report generation of policies and mandates for all the cloud providers we support: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
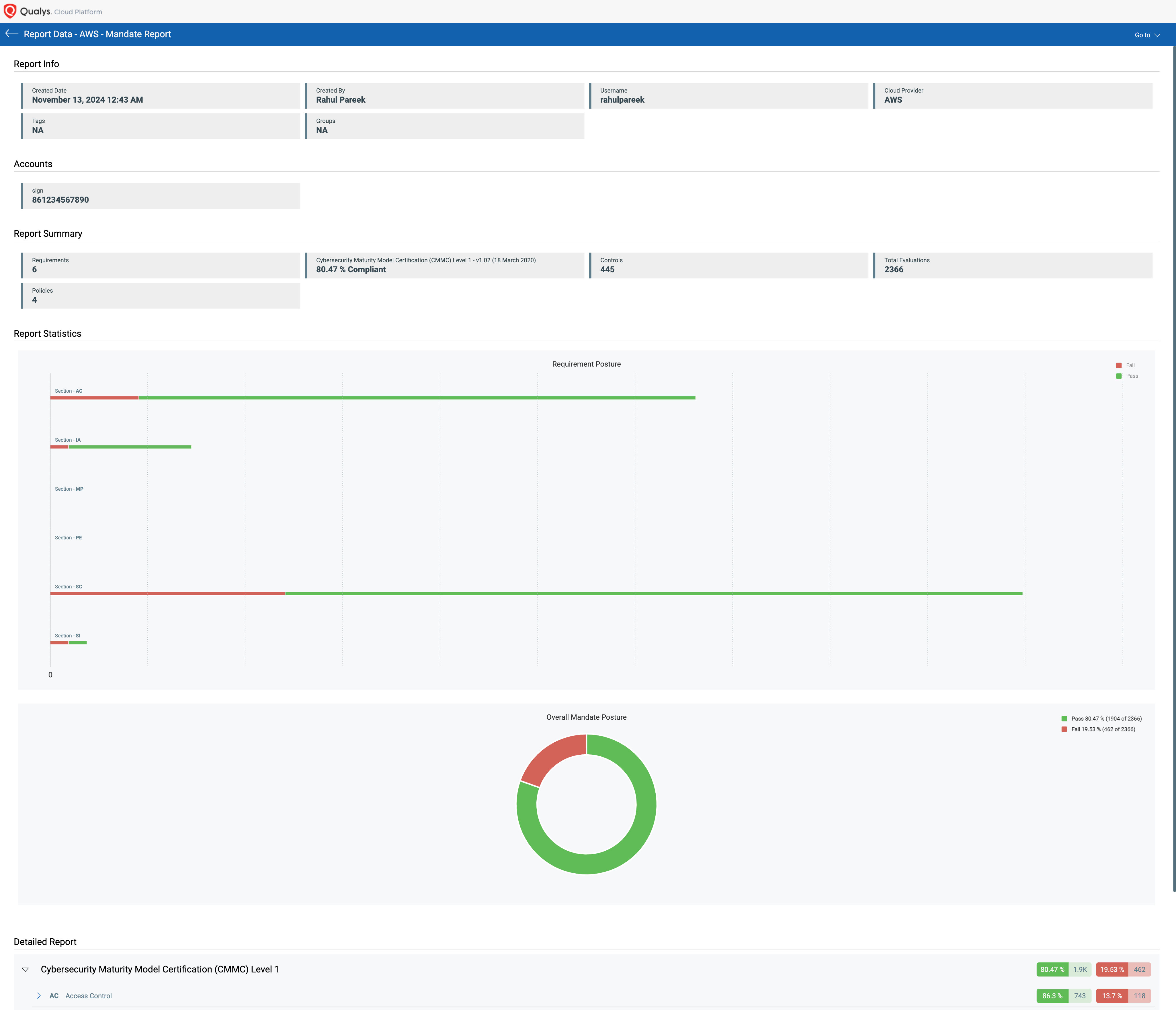
Get complete coverage of CIS foundation benchmarks as well as Qualys best practices and architecture checks, including a breakdown of every control’s security posture, threat inventory at-a-glance, and clear steps to drive remediation. TotalCloud provides coverage of the latest CIS benchmarks across cloud providers.
- CIS Amazon Web Services Foundations Benchmark v3.0.0
- CIS Microsoft Azure Foundations Benchmark v2.1.0
- CIS Google Cloud Platform Foundation Benchmark v3.0.0
- CIS Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Foundations Benchmark v2.0.0
Conclusion
Cloud compliance is essential for organizations leveraging cloud services to meet regulatory requirements, protect sensitive data, and maintain customer trust. By understanding the shared responsibility model, identifying industry-specific regulations, and implementing best practices such as encryption, access control, and regular audits, businesses can create a secure and compliant cloud environment. With the rapid evolution of data privacy laws and cybersecurity threats, achieving and maintaining cloud compliance is an ongoing process that demands continuous monitoring, regular updates to policies, and a proactive approach to risk management. Ultimately, a strong cloud compliance strategy not only mitigates risks but also fosters a culture of accountability and trust, positioning organizations for long-term success in the digital era.
Sign up for a trial to experience first-hand how Qualys TotalCloud can help maintain cloud compliance.
Contributors
- Rahul Pareek, Security Analyst, Cloud, Qualys

Leave a Reply